Fundamentals of Refrigeration: Temperature
Simply defined, temperature is a measurement of the intensity of heat. “Intensity” is an important adjective to use when defining temperature. Everyone is familiar with things feeling “hot” or “cold”, but those terms are subjective and based solely on one’s perception of the intensity of heat energy.

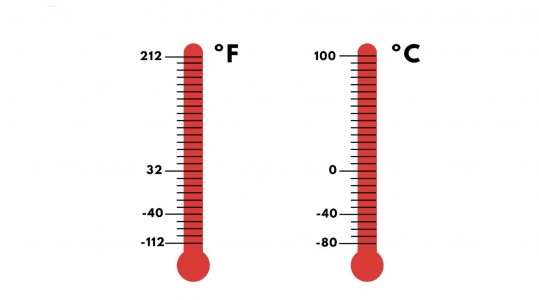
Temperature is measured using a thermometer. In the United States, degrees Fahrenheit are used to measure heat, whereas most other countries use degrees Celsius.

In the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees. In other words, the “intensity of heat” in water must be 212 degrees to cause steam to form.
In the Celsius scale, on the other hand, water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees. The equation to convert from ºC to ºF is:
ºF = 9/5ºC +32
This equation can be rearranged using algebra to convert from ºF to ºC:
ºC = (5÷9)(ºF-32)
Example: Convert 30ºC to ºF.
To find the answer, plug 30 into the Fahrenheit conversion equation. Then, using a calculator, it is determined that 30ºC equals 86ºF.
(9÷5)(30) +32 = 86ºF
For most temperatures encountered on Earth, the Fahrenheit temperature will be a larger number than the equivalent Celsius temperature. An interesting fact is that the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are equivalent at -40 degrees. When the temperature drops below -40 degrees, the Celsius scale has higher values than the Fahrenheit scale.
Both the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are “relative” temperature scales, meaning that they do not measure from absolute zero. Both scales, however, have a counterpart unit that is measured from absolute zero.
ºF can be converted to degrees Rankine (ºR) by adding 459.67 degrees. 0ºR is absolute zero, or the temperature at which there is no heat intensity.
ºC can be converted to Kelvin (K) by adding 273.15. Again, this is an absolute scale, so 0K is the lowest possible temperature. When using the Kelvin or Rankine scale, the numeric values will never be negative.
The Rankine and Kelvin scales are not commonly used in everyday life, but are required for certain scientific calculations. Since the Rankine scale is offset from its Fahrenheit counterpart by a fixed amount, when interacting with temperature differences, it is inconsequential which scale is used.

Example 1:
Convert 40ºF to ºR.
To solve this problem, simply add 459.67 and 40. The answer is 499.67ºR.

Leave a Reply