The Cost of Non-Compliance | Part 7: EPA’s Jurisdiction

Uriah Donaldson presented a technical paper at the 2023 IIAR Conference titled The Cost of Non-Compliance: An Objective Analysis of Federal EPA’s Enforcement at Ammonia Refrigeration Facilities. This blog series includes excerpts from his technical paper.
Part 7: EPA’s Jurisdiction
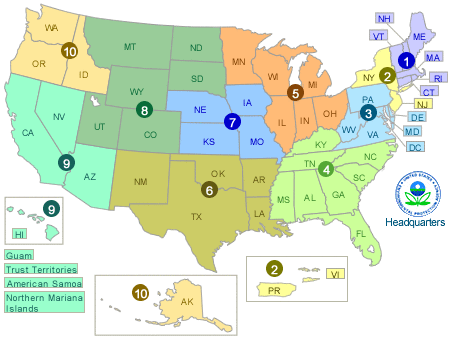
EPA’s 10 Regional Offices
To achieve the EPA’s goals nationwide, ten regional offices were created, each with a specific geographic focus. This geographic focus allows each office to address specific health and environmental concerns within its jurisdiction. The regional offices and their geographic jurisdictions are listed as follows on the Federal EPA website.(37)
- Region 1 – Boston (serving CT, ME, MA, NH, RI, and VT)
- Region 2 – New York City (serving NJ, NY, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands and 8 federally recognized Indian Nations)
- Region 3 – Philadelphia (serving DE, DC, MD, PA, VA, WV and 7 federally recognized tribes)
- Region 4 – Atlanta (serving AL, FL, GA, KY, MS, NC, SC, and TN)
- Region 5 – Chicago (serving IL, IN, MI, MN, OH, and WI)
- Region 6 – Dallas (serving AR, LA, NM, OK, and TX)
- Region 7 – Kansas City (serving IA, KS, MO, and NE)
- Region 8 – Denver (serving CO, MT, ND, SD, UT, and WY)
- Region 9 – San Francisco (serving AZ, CA, HI, NV, American Samoa, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Guam, Marshall Islands, and Republic of Palau)
- Region 10 – Seattle (serving AK, ID, OR, WA and 271 native tribes)
Map of the 10 Regions(38)
Database of Consent Agreements and Final Orders (CAFOs), Expedited Settlement Agreements (ESAs), and Expedited Penalty Action & Consent Agreements (EPACAs)
Two primary types of settlement agreements, a Consent Agreement and Final Order (CAFO) and Expedited Settlement Agreements (ESA), can be used if the EPA inspects a facility and discovers violations. CAFOs are associated with more considerable penalties and sometimes with Supplemental Environmental Projects (SEPs). ESAs are used when a facility has violated one (or more) of EPA’s regulations but only to a small extent; the process is then expedited, and the penalty amount is significantly reduced.
In addition to data on CAFOs and ESAs, the database analyzed in this study contains data on Expedited Penalty Action & Consent Agreements (EPACAs). This type of agreement is only associated in the database with Region 3. This type of agreement also typically includes a small fine (<$5,000) and a larger “fix it” type of penalty. The author is not aware of other regions implementing this type of agreement. In other regions, it is common to require a SEP, which serves the same purposes. Specifically, the facility must spend a certain amount of money on specific projects to bring the facility into compliance. However, sometimes a SEP is required as part of a settlement, but the project benefits local emergency responders rather than producing direct upgrades to the facility.
(37) https://www.epa.gov/aboutepa/regional-and-geographic-offices; (38) https://www.epa.gov/aboutepa/visiting-regional-office
The previous blogs in this series are available in the following links:
- Part 1: Introduction
- Part 2: A Historical Timeline of Major Events (1962-1978)
- Part 3: A Historical Timeline of Major Events (1980-1994)
- Part 4: How the EPA Calculates Civil Penalties – 1984 Policy & Policies for EPCRA and CERCLA
- Part 5: How the EPA Calculates Civil Penalties – Examples of Release Notification and Tier II
- Part 6: EPA’s Combined Enforcement Policy for CAA §112(r) and 40 CFR Part 68

Leave a Reply