Propane and PSM

Question: I am considering installing a propane tank at my facility, will it be subject to the requirements of RMP and PSM?
Answer: Assuming that the propane tank will be used for forklift fuel, you are not required to comply with the requirements of RMP, PSM, or CalARP because of the following exemptions/exclusions:
Title 40 CFR §68.126 A flammable substance listed in Tables 3 and 4 of §68.130 is nevertheless excluded from all provisions of this
part when the substance is used as a fuel or held for sale as a fuel at a retail facility.
Title 29 CFR §1910.119(a)(ii)(A) Hydrocarbon fuels used solely for workplace consumption as a fuel (e.g., propane used for comfort heating, gasoline for vehicle refueling), if such fuels are not a part of a process containing another highly hazardous chemical covered by this standard;
Although exempt from the requirements of RMP, PSM, and CalARP, the propane must be included on all hazardous material inventory reports (e.g. Hazardous Materials Business Plan in California) and employees will be required to be trained for safe handling in accordance with HazCom requirements. Furthermore, the propane tank will be subject to OSHA and EPA’s general duty clause which requires that “each employer shall furnish to each of his employees employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to his employees”
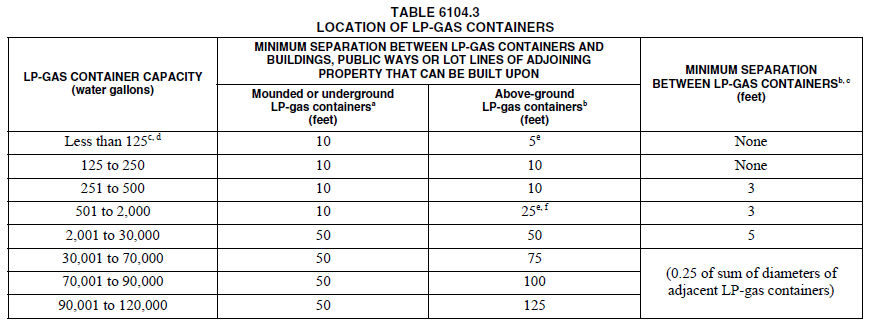
So what are some of the recognized hazards that you should be aware of? Here is a quick overview of select requirements in the 2015 International Fire Code:
1. Impact Protection – The tank will need to be protected from accidental impact. Bollards are the most common type of engineering control used in this regard. Here are the 2015 IFC requirements for Impact Protection:
- Constructed of steel not less than 4 inches (102 mm) in diameter and concrete filled.
- Spaced not more than 4 feet (1219 mm) between posts on center.
- Set not less than 3 feet (914 mm) deep in a concrete footing of not less than a 15-inch (381 mm) diameter.
- Set with the top of the posts not less than 3 feet (914 mm) above ground.
- Located not less than 3 feet (914 mm) from the protected object.
2015 IFC §312.3 Other barriers. Barriers, other than posts specified in Section 312.2, that are designed to resist, deflect or visually deter vehicular impact commensurate with an anticipated impact scenario shall be permitted where approved.
If you are interested in learning more about impact protection, we’ve written about it here.


500 gallon propane tank placed by AmeriGas at a commercial building location. What are the requirements for bollards and what are the fines and fees for non compliance? Plumas county in CA
It is a little dated, but I think this blog will answer your question about bollard location/spacing. As for fines, that can vary greatly based on the inspector, agency, and degree of violation.